| 51 | Heat capacity at constant pressure for ideal gas (Given heat capacity at constant volume) | -502s.png) |
| 52 | Heat capacity at constant volume for ideal gas (given heat capacity at constant pressure) | -503s.png) |
| 53 | Dimensionless heat capacity (given the amount of substance) | -504s.png) |
| 54 | Dimensionless heat capacity (Given the number of molecules in the body) | -505s.png) |
| 55 | Molar heat capacity of an ideal gas (Given degrees of freedom) | -506s.png) |
| 56 | Enthalpy of system (Given Gibbs free energy,internal energy and Helmholtz free energy) | -508s.png) |
| 57 | Internal energy of the system (Given enthalpy,pressure and volume) | -509s.png) |
| 58 | Internal energy of the system (Given Helmholtz free energy,temperature and entropy) | -510s.png) |
| 59 | Internal energy of system (Given Helmholtz free energy,Gibbs free energy and enthalpy) | -511s.png) |
| 60 | Helmholtz free energy (Given internal energy, temperature and entropy) | -512s.png) |
| 61 | Helmholtz energy (Given internal energy, enthalpy and Gibbs free anergy) | -514s.png) |
| 62 | Gibbs energy (Given internal energy, enthalpy and Helmholtz free anergy) | -515s.png) |
| 63 | Entropy of the system (Given Gibbs free energy and enthalpy) | -517s.png) |
| 64 | Entropy of the system (Given Helmholtz free energy and internal energy) | -518s.png) |
| 65 | Change in entropy with constant heat and volume | 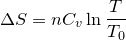 |
| 66 | Change in entropy with constant heat and pressure | 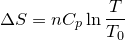 |
| 67 | Change in entropy with constant heat and temperature | 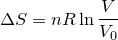 |
| 68 | Change in entropy with constant heat and temperature | 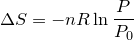 |
| 69 | Change in entropy(specific heat, volume, pressure or temperature is not all constant) | -523s.png) |
| 70 | Change in entropy(specific heat, volume, pressure or temperature is not all constant) | -524s.png) |
| 71 | Efficiency of Carnot heat engine (Carnot's theorem) | -540s.png) |
| 72 | Maximum efficiency of heat engine (efficiency of Carnot heat engine) | -541s.png) |
| 73 | Thermal energy transferred between the hot reservoir and the system (Carnot cycle) | -542s.png) |
| 74 | Thermal energy transferred between the cold reservoir and the system (Carnot cycle) | -543s.png) |
| 75 | The amount of energy transferred as work (Carnot cycle) | -544s.png) |